On March 31, the ImmunizeBC website will move over to HealthLinkBC.ca After this date, you will be automatically redirected to HealthLink BC’s Immunization landing page. HealthLink BC provides trusted health information online and over the phone 24 hours a day, seven days a week by calling 8-1-1.
Date last reviewed:
Friday, Dec 20, 2024
HealthLinkBC
Available in 简体中文 (Simplified Chinese), 繁體中文 (Traditional Chinese), یسراف (Farsi), 한국어 (Korean), ਪੰਜਾਬੀ (Punjabi), and other languages.
Disease it protects against
The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine protects against:
- Infection from 23 types of pneumococcal bacteria.
Pneumococcal infection is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. This bacteria can cause serious and life-threatening infections, including meningitis, an infection of the lining that covers the brain. septicemia, an infection of the blood, and pneumonia, an infection of the lungs. These are serious and life-threatening infections. Learn more about pneumococcal disease.
Fact
Did you know?
Pneumococcal pneumonia kills about 1 in 20 older adults who get it.
Who should get the vaccine
| Age | Schedule |
|---|---|
| Infants & young children |
|
| School-age children & teens |
|
| Adults |
|
A 2nd dose of vaccine is recommended for people with certain medical conditions. Speak with your health care provider to find out if you need a 2nd dose of vaccine and when you should get it.
How well it works
How well the vaccine works depends on your age and general health.
- In older adults and high-risk groups, the protection against a serious infection from pneumococcal disease is 50% to 80%.
When you get immunized, you help protect others as well. People who are immunized are much less likely to catch a preventable disease and spread it to others.
Safety
Vaccine safety is a top priority in Canada. Every vaccine must be shown to be safe and effective before it is approved for use in Canada. After approval, the safety of vaccines is continuously monitored. Learn more about vaccine safety.
Fact
Vaccines are very safe.
Getting the vaccine is much safer than getting pneumococcal disease.
Side effects
Many people have no side effects from vaccines. For those that do, they are usually mild and go away on their own within a few days. Serious side effects are very rare.
Side effects of the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine can include:
-
Soreness, redness and swelling where the vaccine was given.
-
Fever.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is an extremely rare chance of a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. If anaphylaxis happens, you will be given medicine to treat the symptoms.
Let your immunization provider/clinic or health care provider know if you or your child have any serious or unexpected side effects after immunization.
How to manage side effects
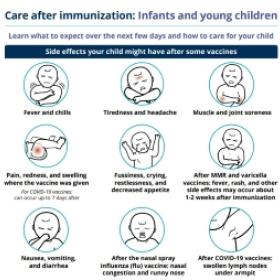
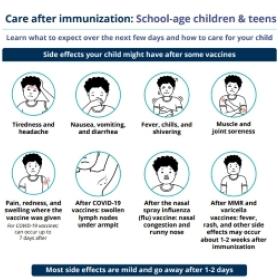
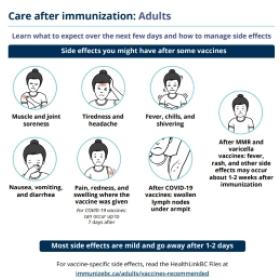
For information on how to manage side effects, view the immunization aftercare sheets below.
Who should not get the vaccine
Speak with your health care provider if you have had a life-threatening reaction to a previous dose of pneumococcal vaccine or any component of the vaccine.
Children under 2 years of age should not receive the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine because it is not effective in young children. These children receive the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine starting at 2 months of age.
There is no need to delay getting immunized because of a cold or other mild illness. However, if you have concerns, speak with your health care provider.
Other vaccines that protect against pneumococcal disease
There are other vaccines that protect against pneumococcal disease:
The pneumococcal conjugate (PCV 13) vaccine protects against infection from 13 types of pneumococcal bacteria. This vaccine is given free to infants at 2, 4, and 12 months of age. It’s also given to older children and adults with certain medical conditions. Learn more about the PCV 13 vaccine.
Other pneumococcal conjugate vaccines have been approved by Health Canada for infants, children, and adults:
- Prevnar®20 (PNEU-C-20).
- Vaxneuvance® (PNEU-C-15).
- CAPVAXIVE ™ (Pneu-C-21) - approved for adults 18 years and older.
These vaccines are not part of BC’s publicly funded (free) vaccine program but can be purchased at some pharmacies and travel clinics. Speak to your health care provider for more information on these vaccines.
Pneumococcal quick facts
- What it is
-
Pneumococcal infection is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. The bacteria can cause serious and life-threatening infections such as meningitis, an infection of the lining that covers the brain, septicemia, an infection of the blood, and pneumonia, an infection of the lungs.Pneumococcal disease is now rare among children in BC because of routine childhood immunization programs.
- How it spreads
-
Pneumococcal infection is spread from one person to another by coughing, sneezing or close face-to-face contact. It can also be spread through saliva when people share food or drinks. Babies and children can become sick through sharing soothers, bottles or toys used by other children.
- Symptoms
-
Symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough - Mucus (sputum) from your lungs may be coughed up. Mucus may be rusty or green or tinged with blood
- Fever
- Fast breathing and fast heart rate
- Chest pain that often feels worse when you cough or breathe in
- Feeling very tired or very weak
Symptoms of pneumococcal meningitis include:- Severe headache
- Fever
- Irritability
- Vomiting
- Neck stiffness
- Risks
-
The bacteria can cause serious and life-threatening infections such as meningitis, an infection of the lining that covers the brain, septicemia, an infection of the blood, and pneumonia, an infection of the lungs. Permanent complications of meningitis include brain damage and deafness.