On March 31, the ImmunizeBC website will move over to HealthLinkBC.ca After this date, you will be automatically redirected to HealthLink BC’s Immunization landing page. HealthLink BC provides trusted health information online and over the phone 24 hours a day, seven days a week by calling 8-1-1.
Date last reviewed:
Tuesday, May 28, 2024
HealthLinkBC
Available in Français (French), Español (Spanish), یسراف (Farsi), 한국어 (Korean), ਪੰਜਾਬੀ (Punjabi), and other languages.

Diseases it protects against
The Td vaccine protects against:
-
Diphtheria
-
Tetanus
These diseases can cause serious illness, hospitalization, and even death. Learn more about these diseases.
Fact
Did you know?
About 1 in 5 people who get tetanus may die.
Who should get the vaccine
| Age | Schedule |
|---|---|
| Adults |
|
If you have a dirty cut or wound, get a tetanus shot as soon as possible if 5 or more years have passed since your last tetanus shot. If you have a serious cut or wound, including punctures, bites, burns or scrapes, it is recommended that you see your health care provider immediately for treatment. This is especially important if the wound is dirty.
Fact
Did you know?
Protection from some vaccines decreases with time. The best way to continue to protect yourself from tetanus and diphtheria is to get a booster dose of the Td vaccine every 10 years.
Safety
Vaccine safety is a top priority in Canada. Every vaccine must be shown to be safe and effective before it is approved for use in Canada. After approval, the safety of vaccines is continuously monitored. Learn more about vaccine safety.
Fact
Vaccines are very safe.
Getting the vaccine is much safer than getting one of the diseases.
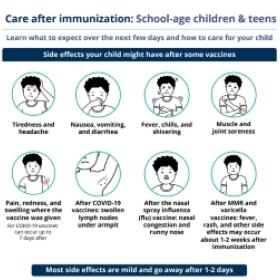
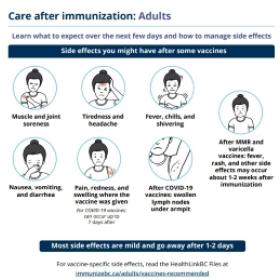
Side effects
Many people have no side effects from vaccines. For those that do, they are usually mild and go away on their own within a few days. Serious side effects are very rare.
Common reactions to the Td vaccine may include:
- Soreness, redness, and swelling where the vaccine was given.
- Fever, headache, and muscle soreness may also occur.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is an extremely rare chance of a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. If anaphylaxis happens, you will be given medicine to treat the symptoms.
Let your immunization provider/clinic or health care provider know if you or your child have any serious or unexpected side effects after immunization.
How to manage side effects
For information on how to manage side effects, view the immunization aftercare sheets below.
Who should not get the vaccine
Speak to your health care provider if you or your child:
- Has had a life-threatening reaction to a previous dose of a tetanus or diphtheria vaccine, or to any component of the vaccine.
- Developed Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) within 8 weeks of getting a tetanus vaccine, without another cause being identified, as you should not get a tetanus-containing vaccine. GBS is a rare condition that can result in weakness and paralysis of the body's muscles. It most commonly occurs after infections, but in rare cases can also occur after some vaccines.
There is no need to delay getting immunized because of a cold or other mild illness. However, if you have concerns, speak to your health care provider.
Information
Immunizations can cause some pain.
This pain can cause stress and anxiety for some adults. Check out some tips you can use to help reduce your pain, stress, and anxiety with immunizations — and make your experience more positive.
Disease quick facts
- Tetanus
-
What is tetanus?
Tetanus is a disease caused by a bacteria that is usually found in dirt and soil. The bacteria make a toxin, or poison, that causes severe muscle spasms. Tetanus can be very dangerous. Tetanus is also called "lockjaw" because muscle spasms in your jaw make it hard to open your mouth.How does tetanus spread?
Tetanus is caused by bacteria usually found in dirt and soil. The bacteria enter the skin through a cut or scrape and produce a poison that causes the painful tightening of the muscles all over the body.Unlike most vaccine-preventable diseases, tetanus does not spread from person to person. Any person not immunized against tetanus is at risk. Immunization is the only way to protect against tetanus.What are the symptoms and risks?
Tetanus symptoms appear slowly and get worse over time. The time it takes for symptoms to appear after a cut or injury ranges from days to months. In most cases, symptoms of tetanus appear within 14 days.Tetanus symptoms often begin with a headache and trouble opening your mouth (lockjaw). You also may have trouble swallowing and/or a stiff neck, back, or shoulders.As the toxin spreads, it can be deadly. It can cause problems with your blood pressure and heart rate. It can cause severe and painful muscle spasms in your neck, arms, legs, and belly.There is no cure for tetanus. Up to 1 in 5 people who get tetanus may die. - Diphtheria
-
What is diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a very serious infection that can affect your nose and throat or skin. It can also spread through the body and damage the heart and central nervous system.Diphtheria is now very rare in Canada because of immunization.How does it spread?
The bacteria are spread through the air by people sneezing or coughing or by direct skin-to-skin contact with someone who has diphtheria.What are the symptoms and risks?
Diphtheria in your nose and throat can cause problems breathing. Symptoms may include:- A moderate to severe sore throat
- Swollen and sore lymph nodes in the neck
- Swelling of the neck
- Heart and nervous system complications
Diphtheria in your skin can cause lesions (damaged skin tissue or sores).Diphtheria can cause severe breathing problems, heart failure and paralysis. One of every 10 people who get diphtheria will die from it.